Understanding Solder Paste for PCB Assembly
Solder paste plays a crucial role in the assembly of printed circuit boards (PCBs). It is used to create solder joints between the electronic components and the printed circuit boards. Solder paste is typically applied to the PCBs using a SMT stencil. After the PCBs are populated typically by a pick and place machine, they are placed in a soldering oven also known as reflow oven. During the reflow process, the PCBs are heated to a specific temperature, causing the solder paste to melt and form a liquid state. The liquid solder then solidifies as it cools, creating a permanent electrical and mechanical connection between the component leads and the PCB pads.
In this article, we will dive into the world of solder paste, exploring the different types available and the significance of solder reflow profiles, also known as thermal profiles in achieving successful PCB assembly.
Solder Paste
Solder paste is a mixture of metal alloy such as tin-lead (Sn-Pb) or lead-free like tin-silver-copper (Sn-Ag-Cu) or tin-copper (Sn-Cu), flux, and a binding agent. The metal alloy provides the necessary conductivity and strength for the solder joints.
The binding agent in solder paste gives it the necessary consistency and adhesion properties. It holds the powdered solder particles and flux together and helps the solder paste adhere to the PCB pads and component leads during PCB assembly.
Solder Paste Types
A common metal alloy still used in solder paste is a combination of tin (Sn) and lead (Pb), commonly known as Sn-Pb solder or leaded solder. However, due to environmental concerns, lead-free alternatives have gained popularity, with tin-silver-copper (Sn-Ag-Cu) and tin-silver (Sn-Ag) alloys being widely used. Hence, current solder paste types can be categorized by their composition as leaded or lead-free:
• Sn-Pb / Leaded Solder Paste: This type of solder paste, consisting of tin and lead, has been the industry standard for many years. It offers excellent wetting properties and relatively low melting temperatures, which make it suitable for a wide range of applications. However, due to environmental regulations restricting the use of lead, Sn-Pb solder paste is gradually being replaced by lead-free alternatives.
• Lead-Free Solder Paste: Lead-free solder pastes have become the preferred choice in modern PCB assembly processes. They comply with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives and offer comparable or even better performance than Sn-Pb solder. The most common lead-free alloy compositions are Sn-Ag-Cu (also known as SAC) and Sn-Ag. These alloys provide reliable solder joints with good mechanical strength and thermal stability.
* Most electronic contract manufacturers in the USA now use lead-free solder paste.
Flux Types
Flux is a chemical compound that cleans and prepares the metal surfaces to be soldered. It removes oxides and contaminants, promoting proper wetting and adhesion of solder to the components and printed circuit board. Flux also acts as a protective layer, preventing further oxidation during soldering and controlling the solder flow to prevent solder bridges. It facilitates heat transfer, ensuring uniform melting and flow of solder for reliable solder joints.
Solder paste can be mixed with the following types of flux:
• Water-Soluble Flux: Which is formulated to be easily cleaned with water or a mild cleaning agent after soldering. It contains organic acids and activators that promote flux activity and solder wetting. Water-soluble flux is commonly used in PCB assembly applications where cleanliness is crucial, such as medical devices or aerospace electronics, as it allows for effective removal of flux residues.
• No-Clean Flux: Which is formulated with a minimal number of activators, reducing the residue left after soldering. The residues produced by no-clean flux are typically non-conductive and non-corrosive, allowing them to remain on the board without causing adverse effects. No-clean flux eliminates the need for post-solder cleaning processes, saving time and cost. It is often used in applications where cleaning may be challenging or unnecessary.
* Most electronic contract manufacturers in the USA use water soluble flux.
| Leaded | Lead-Free | |
| No-Clean |  |  |
| Water Soluble |  |  |
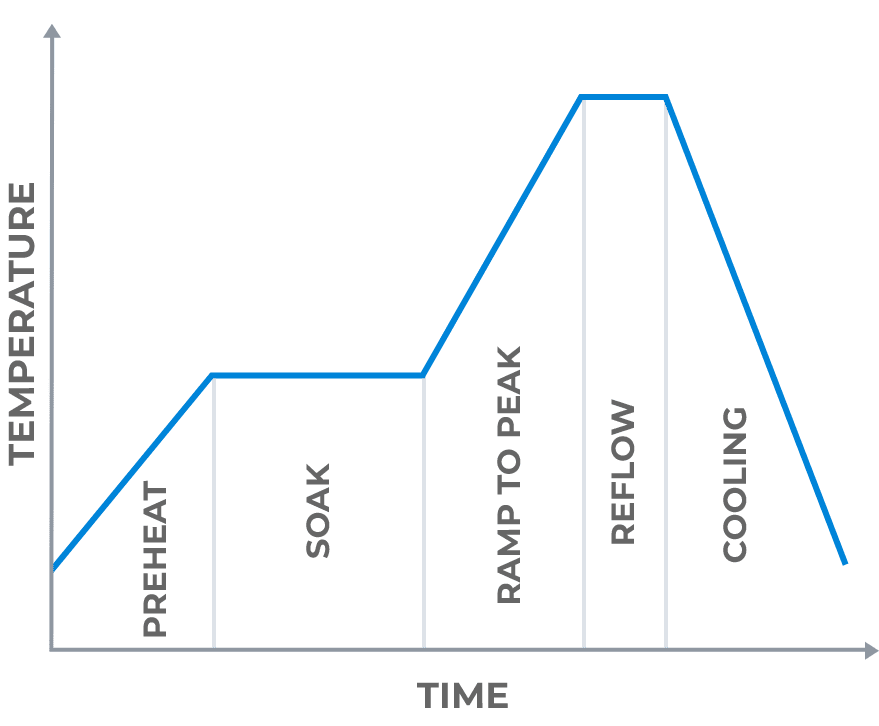
Thermal/Reflow Profiles
Solder reflow is the process by which solder paste transforms from a paste-like consistency to a molten state, creating reliable solder joints between the components and the printed circuit board. To achieve optimal soldering results, a well-defined reflow profile also known as a recipe is crucial. Here are the main stages involved in a typical solder reflow profile:
• Preheat Stage: The preheat stage raises the temperature to remove any moisture or contaminants present on the PCB and components. This step minimizes the risk of thermal shock and promotes good wetting during the subsequent stages.
• Soak Stage: In the soak stage, the temperature is held steady to ensure uniform heating throughout the assembly. This step allows the solder paste to reach a homogeneous molten state and activates the flux. The flux removes any oxides present on the metal surfaces, improving solder wetting and promoting the formation of reliable solder joints.
• Reflow Stage: During the reflow stage, the temperature is rapidly increased to the solder paste’s melting point, causing it to transition from a solid to a liquid state. This stage facilitates the formation of strong intermetallic bonds between the solder and the component leads and PCB pads.
• Cooling Stage: In the final cooling stage, the assembly is gradually brought down to room temperature. Controlled cooling helps prevent thermal stress and the formation of brittle solder joints.
Choosing Solder Paste
PCB Assembly Express is a full-service electronic contract manufacturer (ECM) located in Tualatin, Oregon. We stock all types of solder pastes and fluxes. However, lead-free and water-soluble is by far the most common solder paste/flux combination for all PCB assembly projects. Our team of certified technicians has extensive experience creating reflow profiles for any type of PCB assembly project.
If you have any questions about our reflow process or the specifications of the solder paste we use, feel free to contact us at support@pcbasemblyexpress.com or call at (800) 651-7250.
LEAVE A REPLY